Pound Sterling losses slow as BoE rate decision looms
• GBP/USD eased to 1.3646 on Monday, retreating from the August 2021 high of 1.3847 touched last week as markets position ahead of Thursday's BoE decision.
• BoE widely expected to hold rates at 3.75% on Thursday; markets see less than 50% chance of more than one cut in 2026 amid sticky UK inflation.
• Wednesday will bring the final UK Services PMI data for January, offering fresh insight into inflation pressures.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) took another step lower amid a cautious stance against the US Dollar (USD) on Monday, easing back from recent multi-year highs as investors positioned ahead of a busy week of UK data and the Bank of England's (BoE) first policy decision of 2026. GBP/USD slipped to 1.3646, pulling back from the August 2021 high of 1.3847 reached on January 27, as a firmer Greenback and pre-BoE positioning weighed on Cable.
The BoE is widely expected to hold its Bank Rate unchanged at 3.75% when it announces its decision on Thursday. Markets see only a 4% chance of a rate cut at the February meeting, with the first reduction now priced for April at the earliest. The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) remains divided on the pace of further easing, with December's decision to cut rates a 5-4 split. Governor Andrew Bailey noted that future cuts would become "a closer call" as the Bank Rate approaches neutral levels estimated at 3%-3.5%.
UK inflation data released in January showed that the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for December rose to 3.4% year-on-year, above expectations and complicating the outlook for further rate cuts. Services inflation remains elevated, and while wage growth is moderating, it continues to run above levels consistent with the BoE's 2% inflation target. MPC member Megan Greene cautioned last week that the Bank may not be able to lower rates as much as expected this year.
Tuesday's economic data docket remains limited, forcing Cable traders to wait for Wednesday to bring the final UK Services Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) for January, with flash data showing business activity at a 21-month high. These releases will be closely watched for signs of whether the UK economy's resilient start to 2026 can be sustained amid global uncertainty.
The US Dollar Index (DXY) steadied above 97.00 on Monday following President Donald Trump's nomination of Kevin Warsh as the next Federal Reserve (Fed) Chairman on Friday. Markets view Warsh as a credible, institutionalist pick who would maintain Fed independence, triggering risk-off flows that supported the Greenback. The partial US government shutdown, now in its third day, added to market caution, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) confirming that Friday's Nonfarm Payrolls release has been suspended.
Looking ahead, Sterling traders will focus on Thursday's BoE decision and accompanying Monetary Policy Report for updated guidance on the path of rates. While the Bank is expected to hold steady, any shift in the MPC's tone or updated inflation forecasts could drive GBP volatility. The accompanying quarterly projections will be scrutinized for signs of whether policymakers see scope for faster easing later in the year.
Pound Sterling price forecast
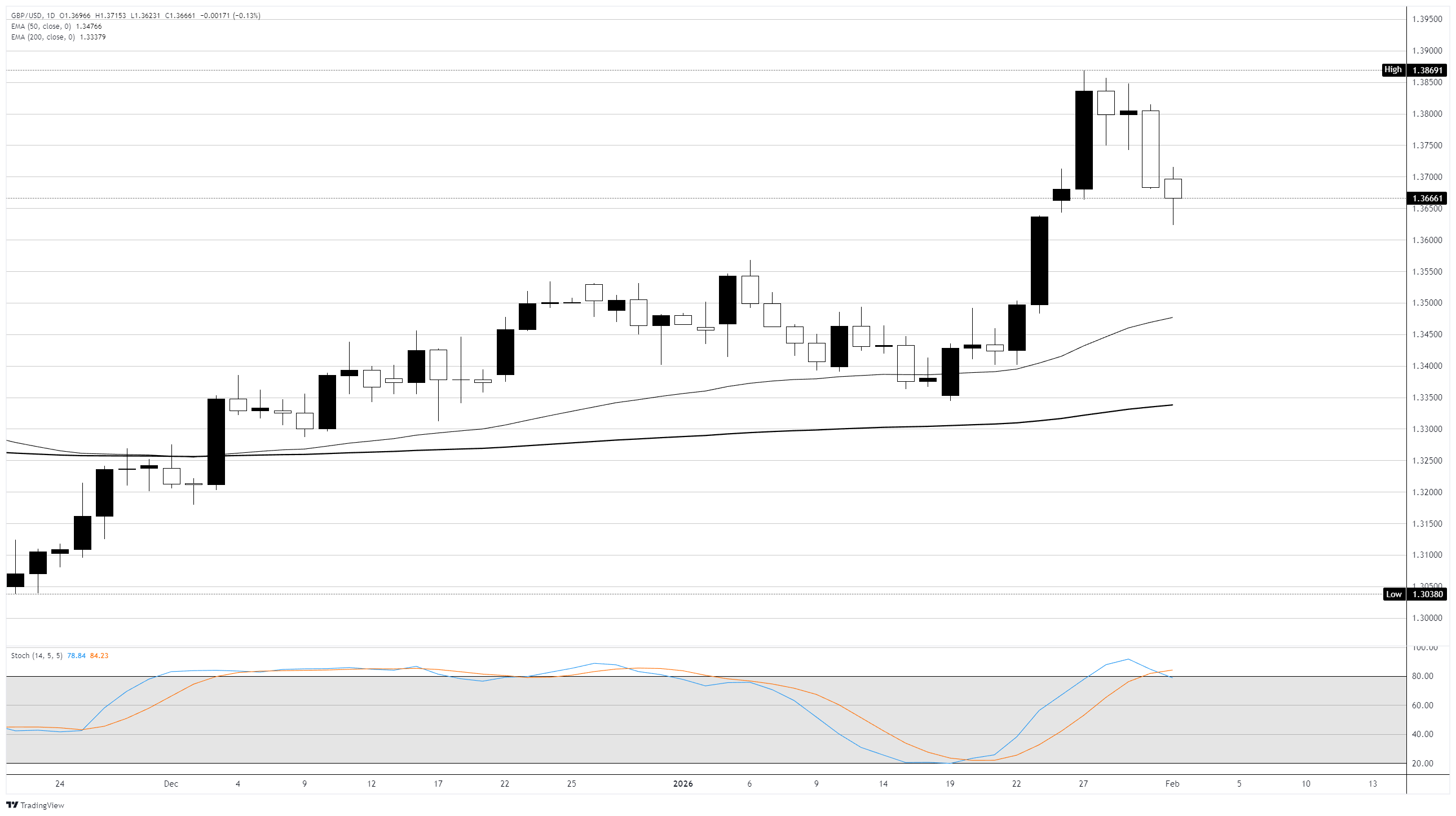
GBP/USD has pulled back from its recent test of the August 2021 high near 1.3847, with the pair now consolidating around the 1.3650 region. The retreat comes after a strong January rally that saw Cable gain over 2% against the Greenback, driven by broad USD weakness and resilient UK data. The 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) has stalled around 1.3680, with price now testing this dynamic support.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) sits near 52, reflecting balanced momentum after the recent pullback from overbought conditions. Measured from the 1.3780 high to the 1.3006 low, the 50% Fibonacci retracement at 1.3393 acts as key support, while the 61.8% retracement at 1.3485 provides an intermediate floor. A close below the latter would signal the recent bullish trend is fading.
Near-term resistance is seen at the 1.3700 psychological level, backed by the January high at 1.3847. Bulls would need a sustained break above this region to open the path toward the 1.4000 handle. On the downside, initial support sits at the 20-day EMA near 1.3680, followed by 1.3485. Thursday's BoE decision could be the catalyst for the next directional move, with any hawkish surprise potentially reigniting Sterling demand.
GBP/USD daily chart
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.







